The concept of potential energy: a complete explanation
The concept of potential energy is fundamental in the study of physics and electricity. It allows us to understand how energy is stored and released in different systems. In this article, we will explore this concept in depth, providing you with a complete explanation that will help you understand its importance and applications in various fields. From gravitational potential energy to electrical potential energy, you will discover how these forms of energy can influence our environment and how we can harness them efficiently. Get ready to enter the fascinating world of potential energy!
What is the concept of potential energy
The concept of potential energy is fundamental in the field of physics and engineering. It refers to the energy that an object possesses due to its position in a force field. In this article, we will explore in detail what exactly potential energy is and how it relates to other key concepts in physics.
Potential energy can be better understood by considering the law of conservation of energy. According to this law, energy is neither created nor destroyed, it is only transformed from one form to another. In the case of potential energy, it is stored in an object due to its position relative to a reference point.
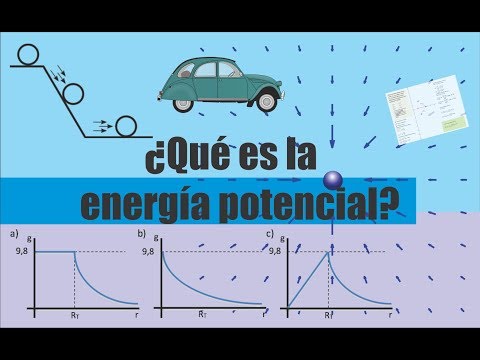
There are different forms of potential energy, depending on the type of force involved. One of the most common forms is gravitational potential energy, which is related to the height of an object above the Earth's surface. The higher an object is, the greater its gravitational potential energy.
Another form of potential energy is elastic energy, which refers to the energy stored in elastic objects, such as springs or rubber bands. When an elastic object is stretched or compressed, elastic potential energy is stored, which is released when the object returns to its original position.
Electrical potential energy is another important type of potential energy. It refers to the energy stored in a system due to the interaction of electrical charges. A common example is the electrical potential energy stored in a capacitor, which is used in many electronic devices.
It is important to note that potential energy is relative to a reference point. The reference point may vary depending on the context. For example, in the case of gravitational potential energy, the reference point is usually the Earth's surface. However, in other cases, such as electrical potential energy, the reference point may be a reference charge or zero electrical potential.
Potential energy can be converted into other forms of energy. For example, gravitational potential energy is converted to kinetic energy when an object falls. Similarly, elastic potential energy is converted to kinetic energy when an elastic object is released and returns to its original position.
What is potential energy and its example
The concept of potential energy: a complete explanation
Potential energy is a fundamental concept in the field of physics and has applications in various fields, such as electronics, mechanics and thermodynamics. In simple terms, potential energy refers to the ability of an object or system to do work due to its position or state.
To better understand this concept, it is useful to consider a concrete example. Imagine a ball at the top of a hill. The ball has the ability to do work as it moves downward due to the Earth's gravitational pull. In this case, the potential energy of the ball is directly related to its height with respect to the ground.
Potential energy can be divided into different forms, depending on the type of energy involved. Some common examples include:
- Gravitational potential energy: As in the ball on the hill example, this form of potential energy is related to the height of an object in a gravitational field.
- Elastic potential energy: This form of potential energy is associated with the deformation of elastic objects, such as a compressed or stretched spring.
- Electric potential energy: refers to energy stored in an electric field, such as in a charged capacitor.
It is important to note that potential energy is a relative measurement and depends on the reference system used. For example, the gravitational potential energy of the ball on the hill will be different if it is measured from a different reference height.
Potential energy can be converted to other forms of energy, such as kinetic energy, when work is done on an object or system. For example, when the ball rolls down the hill, its gravitational potential energy is converted to kinetic energy.
How potential energy is produced
The concept of potential energy: a complete explanation
Potential energy is a fundamental concept in physics that describes the ability of an object to do work due to its position or state. Simply put, it is the energy stored in a system that can be converted to kinetic energy when released.
To understand how potential energy is produced, we must consider two main aspects: gravitational force and height. The gravitational force acts on an object depending on its mass and the acceleration due to gravity. As an object rises in a gravitational field, the gravitational force decreases and therefore the work done by this force also decreases. This means that the object is gaining potential energy as it rises.
Height also plays a crucial role in potential energy production. The higher the height of an object, the greater its potential energy. This is because height represents the vertical distance from the object to a reference point, such as the ground or the zero potential energy level. The higher an object is, the more potential energy it has stored.
A common example to illustrate this concept is that of an object at rest on an elevated platform. In this case, the potential energy of the object is due solely to its height relative to the ground. If the object is released and falls, this potential energy is converted to kinetic energy as the object gains speed. Kinetic energy is calculated using the formula 1/2 * mass * velocity squared.
Importantly, potential energy does not only apply to objects in the Earth's gravitational field. It can also be applied to electrical, magnetic and elastic systems, among others. In each case, potential energy relates to the properties of the system and the ability to store energy in a potentially usable form.
And so, friends, we discovered the incredible hidden power that objects at rest have! Potential energy is like the secret superpower of physics, waiting patiently to be released. You know, the next time you see a rock at the top of a hill, remember that it may be conspiring to roll and wreak havoc. Be careful with the rocks!

Post Comment