Series and parallel circuits: What are they and how do they work?
Series and parallel circuits are fundamental concepts in the world of electronics. Although they may seem complicated at first, understanding how they work is essential for anyone interested in the design and construction of electrical circuits. In this article, we will explore in detail what series and parallel circuits are, how they differ, and how they affect the flow of current in a circuit. Read on to find out everything you need to know about these basic circuits!
What is the series circuit and how does it work?
What are series and parallel circuits and how do they work?
In the world of electronics, it is essential to understand how series and parallel circuits work. These are two connection types that are commonly used to connect electronic components and create more complex systems.
What is a series circuit
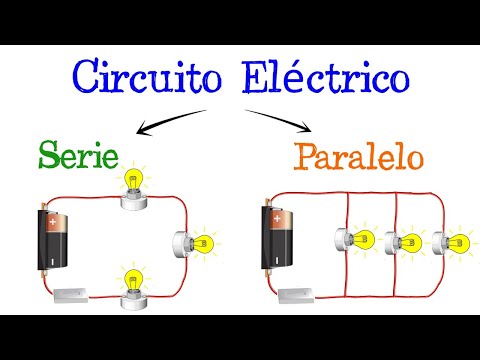
A series circuit is one in which the components are connected one after another, so that the electric current flows through each of them in the same direction. This means that the current is the same in all components of the series circuit.
In a series circuit, the total resistance is the sum of the individual resistances of each component. This means that as more resistors are added in series, the total resistance of the circuit increases.
What is a parallel circuit
A parallel circuit is one in which the components are connected in such a way that each of them is connected directly to the terminals of the power supply. In a parallel circuit, the current is divided between the different components, but the voltage is the same in all of them.
In a parallel circuit, the total resistance is less than the individual resistance of each component. As more resistors are added in parallel, the total resistance of the circuit decreases.
Comparison between series and parallel circuits
- Series circuits: The current is the same in all components. The total resistance is the sum of the individual resistances.
- Parallel circuits: The current is divided between the components. The total resistance is less than the individual resistance.
How does a parallel circuit work?
Series and parallel circuits: What are they and how do they work?
Series and parallel circuits are common configurations in electronics and electricity. These configurations are used to connect electronic components and create functional circuits. In this article, we are going to focus on how a parallel circuit works.
What is a parallel circuit?
A parallel circuit is one in which the components are connected in parallel, that is, each of them is connected directly to the same connection points. In a parallel circuit, the current is divided between the connected components, but the voltage across each component is the same.
How does a parallel circuit work?
When components are connected in parallel, the current is divided between them. This is because the current has multiple paths to flow. The total current entering the circuit is divided between the connected components, according to their individual resistances. It is important to note that the sum of the currents flowing through the parallel components is equal to the total current entering the circuit.
In a parallel circuit, the voltage across each component is the same. This is because all components are connected directly to the same connection points. The total voltage applied to the circuit is divided equally between the connected components.
Advantages of parallel circuits
Parallel circuits have several important advantages. One advantage is that if one component fails in a parallel circuit, the other components can continue to operate without interruption. This is because the components are connected in parallel and do not depend on each other to function.
Another advantage of parallel circuits is that the total resistance of the circuit decreases as more components are added. This means that the total current increases, which can be beneficial in certain applications.
Parallel Circuit Example
To illustrate how a parallel circuit works, let's consider the following example. Suppose we have three light bulbs connected in parallel to a power source. If one of the bulbs burns out, the other two will continue to work without problems. Additionally, the voltage on each bulb will be the same, ensuring uniform brightness.
How to make a series circuit
Series and parallel circuits: What are they and how do they work?
In the world of electronics, it is important to understand how components connect to form circuits. Two of the most common configurations are series and parallel circuits. In this article, we will explain what these types of circuits are and how they work.
Series circuits
A series circuit is one in which components are connected one after another, so that current flows through each component in the same path. In other words, the same current passes through all components of the circuit.
To build a series circuit, we simply connect the positive terminal of one component to the negative terminal of the next. This creates a continuous chain of interconnected components.
In a series circuit, the current is constant in all components, while the voltage is divided between them. This means that the sum of the individual voltages of each component is equal to the total voltage of the circuit.
A common example of a series circuit is Christmas lights. All the lights are connected in a chain, so if one goes out, all the others go out too.
Parallel circuits
In contrast, a parallel circuit is one in which the components are connected so that the current is divided between them. Each component has its own path for current, but they share the same voltage.
To build a parallel circuit, we simply connect the positive terminal of all the components to the positive terminal of the power supply and the negative terminal of all the components to the negative terminal of the power supply.
In a parallel circuit, the current is divided between the components, while the voltage is the same across all of them. This means that the sum of the individual currents of each component is equal to the total current of the circuit.
A common example of a parallel circuit is that of electrical outlets in a house. Each socket has its own path for current, but they all share the same mains voltage.
So now you are an expert in series and parallel circuits! You know how they work and how they connect. Now you can impress your friends with your electronic knowledge. But beware! Don't get too excited and start building your own giant robot. Remember, it's always best to leave that to the professionals. Keep learning and having fun with electronics!



Post Comment