How the 4-Stroke Diesel Engine Works: A Complete Guide
Discover with us the fascinating world of how the 4-stroke diesel engine works. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore step-by-step how this innovative system powers modern machinery. Join us on this journey of knowledge in Polarities!
How the diesel cycle engine works: everything you need to know
How the diesel cycle engine works: everything you need to know
The diesel cycle engine is a type of internal combustion engine that is commonly used in diesel vehicles, heavy machinery, and in industrial applications. Unlike gasoline engines, diesel engines do not use spark plugs to ignite the air-fuel mixture; instead, ignition occurs by compressing the air in the cylinder.
Operating principle:
In a diesel engine, air is drawn into the cylinder during the intake stroke. Once the air has been compressed inside the cylinder, high-pressure diesel fuel is injected. The air-fuel mixture ignites due to the high temperature generated by compression, causing combustion and expansion of the gases.
Main components:
– Cylinders: where combustion takes place.
– Piston: moves inside the cylinder to compress air and fuel.
– Cylinder head: covers the upper part of the cylinder and contains the intake and exhaust valves.
– Injection system: responsible for supplying fuel to the cylinder.
– Exhaust system: eliminates combustion gases.
Advantages of diesel engine:
– Greater thermal efficiency.
– Greater durability and useful life.
– Better performance in heavy load applications.
Disadvantages of diesel engine:
– Higher level of noise and vibrations.
– Higher initial cost.
– Polluting emissions.
The principle of operation of a diesel engine: how combustion occurs
In a diesel engine, combustion occurs as follows:
- The process begins when air is drawn into the combustion chamber.
- In the combustion chamber, air is compressed to high pressure by the piston which moves upward on the compression stroke.
- Once the air is compressed, diesel fuel is injected into the chamber through an injector.
- Diesel fuel is atomized and mixed with highly compressed air.
- Ignition then occurs: due to the high temperature generated by compression, the fuel ignites spontaneously.
- The air and fuel mixture burns in a controlled manner, generating the energy necessary for the engine to run.
This process is essential in diesel engines, since efficient combustion guarantees optimal engine performance and lower emissions of pollutants.
How the 4-stroke diesel engine works: a detailed explanation
How the 4-stroke diesel engine works: a detailed explanation
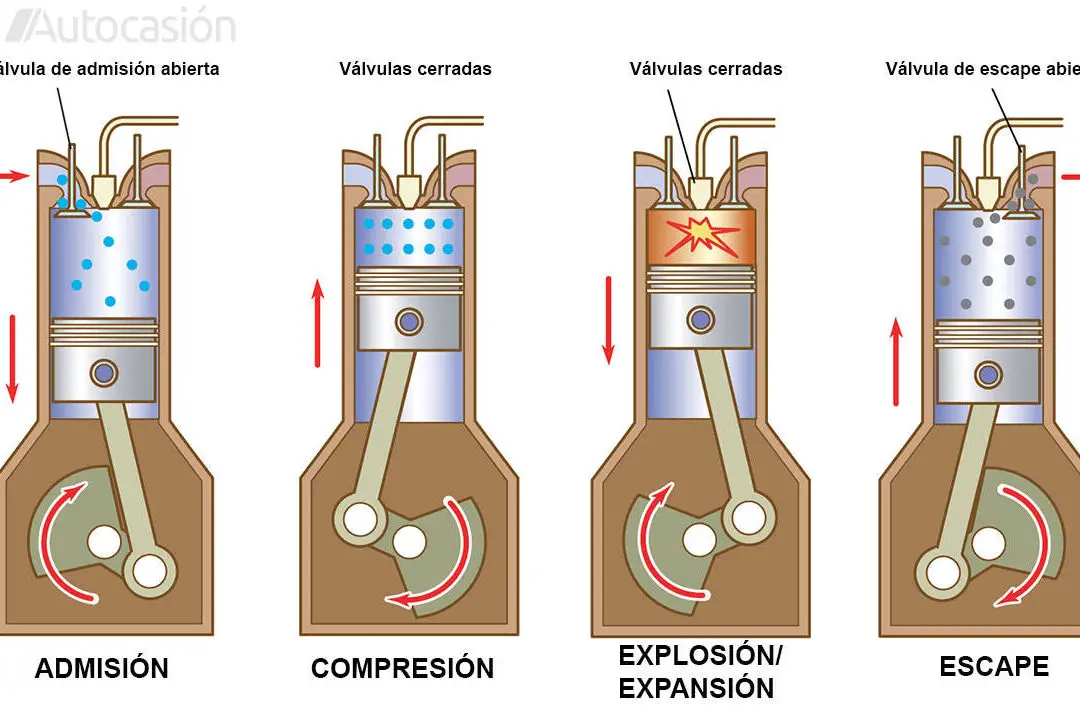
A 4-stroke diesel engine is a type of internal combustion engine that operates in four different stages to generate power from diesel fuel. Below are the four key stages of this process:
- Admission: In this first stage, the piston descends and creates a vacuum in the cylinder, allowing air to enter the combustion chamber through the intake valve. The air is compressed as the piston moves upward.
- Compression: Once air has entered the cylinder, the piston moves upward compressing the air. High compression generates high temperatures in the combustion chamber.
- Combustion: In this crucial stage, diesel fuel is injected into the combustion chamber at high pressure through the injector. The fuel is ignited by the high temperature generated during compression, which causes controlled combustion and an expansion of gases that push the piston down.
- Escape: Finally, in the last stage, the exhaust gases resulting from combustion are expelled from the cylinder through the exhaust valve as the piston moves upward again. This exhaust process prepares the cylinder for a new intake and compression sequence.
And that's how the 4-stroke diesel engine works its magic to make your car move like lightning! Now you can show off to your colleagues everything you know about engines. Step on the accelerator and ride like a champion!


Post Comment