The transfer function in buck converters: A complete analysis
The transfer function in buck converters: A complete analysis
In the fascinating world of power electronics, buck converters occupy a prominent place. These devices are widely used in various applications, from powering electronic equipment to charging batteries. But have you ever wondered how a buck converter actually works and what its transfer function is? In this comprehensive review, we will explore this fundamental concept in detail, unlocking all the secrets behind the magic of buck converters. Get ready to embark on an exciting journey into the world of power electronics!
The buck converter: a complete guide to its operation and applications
The buck converter is an electronic device used in the conversion of electrical energy. Its operation is based on the principle of switching, which allows it to regulate the output voltage from a constant input voltage source.
This type of converter is widely used in various applications, since it is capable of reducing the input voltage to a desired level. This makes it a very useful tool in low voltage power systems, such as battery charging.
The operation of the buck converter is based on the use of a controlled switch, which allows the time relationship between the input voltage and the output voltage to be regulated. When the switch is closed, the input voltage is applied to the load, while when the switch is open, the input voltage is locked and the output voltage remains constant.
One of the most notable advantages of the buck converter is its efficiency. Due to its ability to regulate the output voltage, this device minimizes power losses, resulting in higher performance compared to other types of converters.
Furthermore, the buck converter is highly versatile, since it can be used in both direct current and alternating current systems. This gives it a wide range of applications in different industries, such as automotive, consumer electronics and renewable energy.
Some of the most common buck converter applications include charging batteries in electric vehicles, regulating voltage in photovoltaic systems, and powering low-power electronic devices.
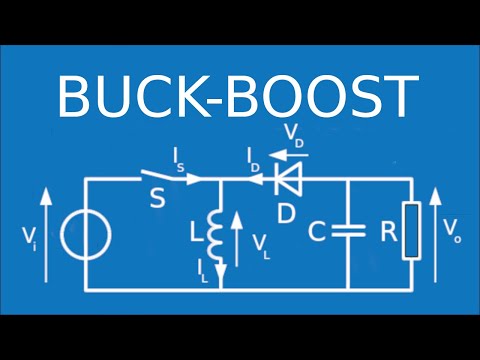
The Buck-Boost Converter System: A Complete Guide to Understanding How It Works
In the world of electronics and energy, there are different converter systems that allow the electrical voltage or current to be modified to adapt it to the specific needs of a circuit or device. One of the most used systems is the Buck-Boost converter, which has the ability to increase or decrease the input voltage efficiently.
What is a Buck-Boost converter system?
The Buck-Boost converter is a type of DC-DC (direct current to direct current) converter that allows the output voltage to be regulated depending on the input voltage. Unlike traditional converters, which can only increase or decrease the input voltage, the Buck-Boost has the ability to perform both functions.
How does the Buck-Boost converter system work?
The operation of the Buck-Boost converter is based on a controlled switch, which is responsible for connecting and disconnecting the load from the circuit periodically. When the switch is closed, current flows through the load and energy is stored in the inductor. On the other hand, when the switch is opened, the current is reversed and the energy stored in the inductor is used to keep the current constant.
Buck-Boost Converter System Applications
The Buck-Boost converter system has a wide range of applications in different fields of electronics and energy. Some of the most common applications are:
– Battery power systems: The Buck-Boost converter is used to regulate the voltage of batteries and ensure a constant supply of power to electronic devices.
– Battery charging: used in battery charging systems to adjust the input voltage and ensure safe and efficient charging.
– LED lighting systems: the Buck-Boost converter is used to regulate the input voltage of LED lighting systems, allowing precise control of light intensity.
– Solar energy systems: used to adapt the voltage of the solar panels to the requirements of the energy storage systems or inverters.
– Telecommunications systems: The Buck-Boost converter is used in telecommunications systems to regulate the input voltage and ensure a stable and efficient power supply.
How the fly back works: everything you need to know
The fly back, also known as a flyback transformer, is an essential component in many electronic devices, such as televisions and CRT (cathode ray tube) monitors, as well as switching power supplies. In this article, we will explain everything you need to know about how this key component works.
The fly back is a type of transformer that is used to generate the high voltage necessary to power the screen of a television or CRT monitor. Its name comes from the way it works: when the current through the primary winding is abruptly interrupted, the energy stored in the transformer's magnetic field is released into the secondary winding in the form of a high voltage.
Operating principle
The fly back consists of several key components, including a ferrite core, two windings (primary and secondary), and a blocking diode. During the operating cycle, current flows through the primary winding, creating a magnetic field in the ferrite core. When the current is turned off, the magnetic field collapses rapidly, generating a high voltage in the secondary winding. This high voltage is rectified and filtered to power the television screen or CRT monitor.
Applications
The fly back is mainly used in CRT devices, but it is also found in switching power supplies, where it is responsible for generating the voltages necessary to power the different components of the circuit. In CRT televisions and monitors, the fly back is responsible for generating the high voltage necessary to accelerate the electrons and cause them to impact the screen, thus creating the images we see.
Security considerations
It is important to note that fly back generates extremely high voltages, which can be dangerous if not handled properly. Therefore, if you do not have experience handling high-voltage electronic components, it is advisable to leave any repair or maintenance related to the fly back in the hands of a professional.
Say goodbye to voltage limits with Buck converters! In this article we've broken down the transfer function of these ingenious devices, and now we're ready to say goodbye to those high voltages like saying goodbye to a bad movie.
So now you know, if you are tired of those high voltages that make you sweat bullets, Buck converters are your solution. These guys will help you reduce the voltage like it's child's play.
Now you can enjoy a life without overloads, without worrying about those voltage spikes that scare you more than a horror movie. Thanks to the transfer function of Buck converters, you will be able to keep your electronic devices running smoothly and without your electricity bill giving you a heart attack.
So now you know, if you want to forget about those voltages that give you more headaches than excess caffeine, Buck converters are your best ally. Say goodbye to problems and hello to a calmer life with less stress!
And remember, if you want to continue learning about the wonders of electronics and discover how other fascinating devices work, do not hesitate to visit our blog at www.polaridad.es. We are waiting for you with open arms (and voltages)!



Post Comment